Take this Mitochondria Quiz to find out how well you know the cell structure. We update the quiz regularly and it’s the most accurate among the other quizzes.
Mitochondria are commonly referred to as the cell’s powerhouses. They aid in the conversion of the energy we obtain from meals into energy that the cell can utilize. However, mitochondria are responsible for more than only energy production.
Mitochondria, which are found in nearly all types of human cells, are critical to our life. They provide the majority of our adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s energy currency.
Mitochondria are also engaged in other processes, such as cell signaling and cell death, commonly known as apoptosis.
In this post, we’ll look at how mitochondria work, what they look like, and what happens when they don’t do their job properly.
Mitochondria are small, usually between 0.75 to 3 micrometers in size, and are not visible under a microscope unless dyed.
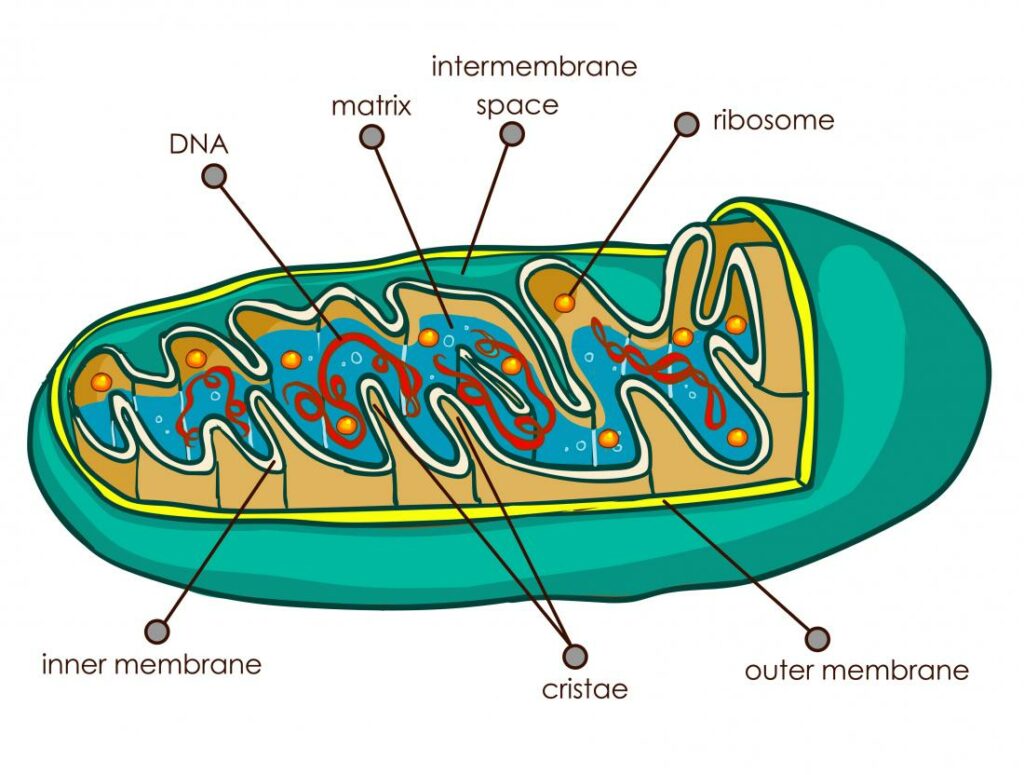
They have two membranes, one on the outside and one on the inside, unlike other organelles (miniature organs within the cell). Each membrane serves a distinct purpose.
Mitochondria are divided into compartments or regions, each of which performs a specific function.
Mitochondria Quiz
The following are some of the major regions:
The outer membrane allows small molecules to move freely across it. Porins, which form channels that allow proteins to traverse, are found in this outer section. The outer membrane also contains a number of enzymes that perform a range of activities.
The intermembranous space is the space between the inner and outer membranes.
Inner membrane: This membrane contains proteins that serve a variety of functions. The inner membrane is impervious to most molecules because it lacks porins. Only molecules in specific membrane transporters can pass the inner membrane. The inner membrane is where the majority of ATP is produced.
Cristae: These are the inner membrane folds. They enhance the membrane’s surface area, hence increasing the space accessible for chemical processes.
The inner membrane’s matrix is the space within it. It is essential in the synthesis of ATP and contains hundreds of enzymes. Mitochondrial DNA is stored in this compartment (see below).
The quantity of mitochondria in each cell type varies. For example, adult red blood cells have none, whereas liver cells can have over 2,000. Cells with a high energy demand have a bigger number of mitochondria. Mitochondria consume around 40% of the cytoplasm in cardiac muscle cells. Also, you must try to play this Mitochondria Quiz.
Despite the fact that mitochondria are commonly depicted as oval-shaped organelles, they are constantly dividing (fissioning) and merging together (fusion). As a result, these organelles are connected in ever-changing networks.
In addition, the mitochondria in sperm cells are coiled in the midpiece and supply energy for tail motion.
What exactly do mitochondria do?
Although the most well-known function of mitochondria is energy production, they also perform other critical functions.
In fact, only roughly 3% of the genes required to create a mitochondrion are found in its energy-producing machinery. The vast majority are engaged in additional tasks that are unique to the cell type in which they are present.
About the quiz
We’ll go through a couple of the mitochondria’s functions below:
Creating energy
Because it powers metabolic processes, ATP, a complex organic molecule found in all forms of life, is often referred to as the molecular unit of currency. The citric acid cycle, often known as the Krebs cycle, is responsible for the majority of ATP production in mitochondria.
The folds or cristae of the inner membrane are the primary sites of energy production.
Mitochondria are organelles that convert chemical energy from the food we eat into energy that the cell can use. This is known as oxidative phosphorylation.
NADH is a molecule that is produced by the Krebs cycle. NADH is converted into ATP by enzymes located in the cristae. Energy is stored in the form of chemical bonds in ATP molecules. The energy can be used when these chemical bonds are broken.
Death of cells
Cell death, also known as apoptosis, is a necessary aspect of life. Cells are cleaned away and destroyed as they get old or broken. Mitochondria play a role in determining which cells are killed.
Mitochondria produce cytochrome C, which activates caspase, one of the main enzymes involved in cell death during apoptosis.
Because certain disorders, such as cancer, involve a breakdown in normal apoptosis, mitochondria are thought to be involved.
For more personality quizzes check this: George Washington Quiz