Take this Greek Mythology Quiz to find out can you answer all the questions. We update the quiz regularly and it’s the most accurate among the other quizzes.
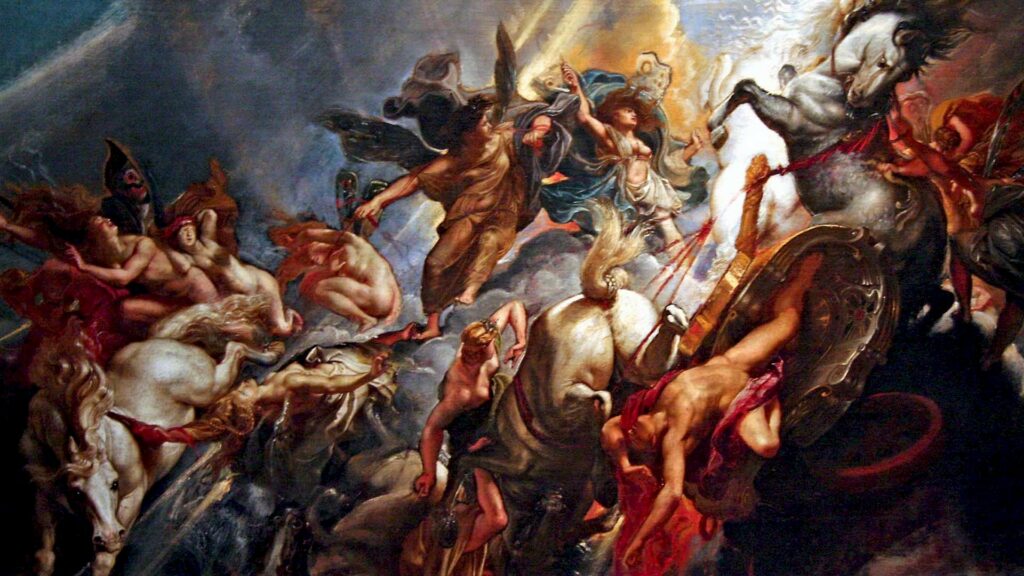
Greek mythology was used to explain the environment in which humans lived, natural phenomena they observed, and the passage of time through the days, months, and seasons. Greek myths were also inextricably linked to religion, explaining the origins and lives of the gods, as well as where humanity had come from and where it was going after death.
Greek myths not only gave the gods of Greek religion faces and personalities, but they also provided people with useful practical advice on how to live a happy life. Another function of myths was to retell historical events so that people could keep in touch with their ancestors, the wars they fought in, and the places they explored. Also, you must try to play this Greek Mythology Quiz.
Greek Mythology Quiz
The Transmission of Myths
In modern usage, the term “myth” may have negative connotations, implying a lack of authenticity and dependability. However, it should not be assumed that myths were universally accepted, nor that the Greeks were completely dismissive of them. As with any religious or non-written source, the Greek myths were probably believed by some and rejected by others. Myths were undoubtedly used for religious and educational purposes, but they could also have served a purely aesthetic function of entertainment. What is certain is that the myths were familiar and popular to a large segment of Greek society due to their widespread representation in art, whether as sculpture on public buildings or scenes painted on pottery.
Without widespread literacy, myths were first passed down orally, most likely by Minoan and Mycenaean bards beginning in the 18th century BCE. This, of course, opens the door to the possibility that each retelling of a specific myth is embellished and improved upon in order to increase audience interest or incorporate local events and prejudices. However, this is also a modern interpretation, because it is possible that the telling of myths followed certain presentation rules, and a knowledgeable audience would not have willingly accepted ad hoc adaptations to a familiar tale. However, with increasing contact between city-states over the centuries, it is difficult to imagine that local stories did not become mixed with others to create a myth with multiple origins.
About the quiz
Around the 8th century BCE, the creation of poems in Ionia and the celebrated poems of Homer and Hesiod marked the next step in the presentation of myths. Mythology was presented in written form for the first time. The Iliad of Homer recounts the final stages of the Trojan War – possibly an amalgamation of many conflicts between Greeks and their eastern neighbors in the late Bronze Age (1800-1200 BCE), while the Odyssey recounts the hero Odysseus’ long journey home after the Trojan War. Hesiod’s Theogony is a genealogy of the gods, and his Works and Days is a description of man’s creation. Not only are gods described as having typical human emotions and failings, but heroes are also created, often with one divine parent and the other mortal, providing a link between man and the gods.
From the 8th century BCE onwards, pottery was the primary medium for representing myths. A plethora of mythical scenes decorate ceramics of all shapes and functions, ensuring that the myths reached a wider audience.
Greek mythology remained popular throughout the centuries, and major public buildings such as the Parthenon in Athens, the Temple of Zeus in Olympia, and the Temple to Apollo in Delphi were decorated with larger-than-life sculptures depicting famous mythological scenes. The myths were presented in the new format of theatre in the 5th century BCE, particularly in the works of the three tragedians Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides. Simultaneously, beginning in the sixth century BCE, the first documented skepticism and even rejection of myths began with pre-Socratic philosophers seeking a more scientific explanation for phenomena and events. Finally, in the fifth century BCE, the first historians Herodotus and Thucydides sought to document events as accurately as possible and record a less subjective view of events for posterity, and thus the modern subject of history was born.
For more personality quizzes check this: Which Turning Red Character Are You?