Take this Attachment style quiz to find out. We update the quiz regularly and it’s the most accurate among the other quizzes.
As a result, people have different attachment styles. This is based on the attachment theory, which was first developed in the 1950s by psychologist Mary Ainsworth and psychiatrist John Bowlby. Our attachment style as adults is regarded to be a reflection of our relationship with our caregivers as infants and children.
Alyssa “Lia” Mancao, LCSW, believes that attachment style encompasses our emotional responses to others as well as our behaviors and interactions with them.
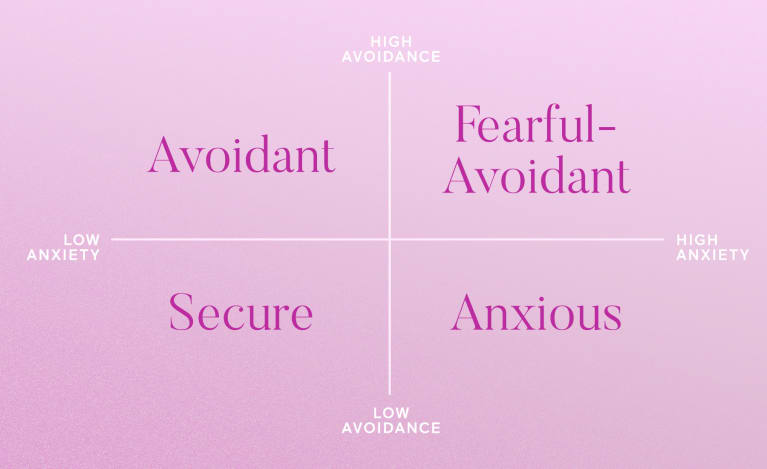
There are four basic types of adult attachment: secure, anxious, avoidant, and fearful-avoidant attachment styles, according to research.
Relationships don’t frighten them, and neither do partners’ requests for privacy. It is possible to depend on others without being totally dependent on them, which is a rare talent.
Researchers Cindy Hazan and Phillip Shaver found that about 56 percent of adults have a secure attachment type in the 1980s.
Some 19 percent of adults, according to Hazan and Shaver’s research, show an anxious attachment type.
“Attachment” is defined by John Bowlby as “a permanent psychological connection between human beings”
Early childhood experiences, according to Bowlby, have a significant impact on subsequent development and behavior.
Attachment style quiz
A baby’s relationship with a caregiver shapes our early attachment styles in childhood. To this end, Bowlby considered that attachment had a survival value. Also, people are wired for emotional attachments, he said, which is a part of their nature.
There are three major statements concerning attachment theory that Bowlby made as well. It was first hypothesized that children raised in an environment where they knew their primary caregiver will be available were less likely to suffer dread than those reared in an environment where they were uncertain.
During that time, a person’s expectations tend to remain pretty constant throughout the remainder of their life.
Because their caregivers have responded in the past, youngsters develop the expectation that they will be responsive to them. Also, you must try to play this Attachment style quiz.
As they go through life’s transitions, from the ridiculous to the monumental, a group of imperfect but endearing New Yorkers struggles to find (or hold on to) love. A sitcom that’s humorous, heartwarming, and sometimes affecting.
Most of all, it’s a fantastic example of how people form attachments.
Please do not be alarmed if you do not know what attachment styles are or if you have not seen the presentation before. Individuals or groups of individuals will recognize themselves or others after hearing the characters and how they personify each attachment style.
But first, let’s define the term “attachment.” With our first primary caregiver, generally a parent, we develop attachment. Ubiquitous human phenomena begin in the womb and affect how we find, keep, and end relationships in adulthood.
About the quiz
There are questionnaires you may take to determine your attachment style (like this one). These comments include: “I quickly form emotional attachments to other people”; “If a partner presses me to commit, I freak out”; and “If I’m not in a relationship, I’m nothing.” In the context of relationships and intimacy, these items probe our perceptions of others and ourselves.
Fear of closeness defines the avoidant attachment type, an insecure attachment style. With an avoidant attachment style, people often find it difficult to get close to others or to trust them in a romantic or friendship setting. Relationships with them are often distant or emotionally unavailable since they desire to be autonomous and self-reliant.
Attachment avoidance, or dismissive-avoidant attachment, is similar to the anxious-avoidant attachment type that is common in children and young adults. According to Hazan and Shaver, about 25 percent of individuals exhibit the avoidant attachment type of attachment style.
There are two attachment styles: anxious and avoidant. Affection is something that people with fearful-avoidant attachment seek, but also want to avoid at all costs. A close romantic relationship is something they’re reluctant to pursue, yet they have a strong need to be loved by other people.
Disorganized attachment, also known as fear-avoidant attachment, is extremely rare and poorly understood. We do know, however, that it is related to severe psychological and relational concerns, including increased sexual behavior, an increased risk for violence in their relationships, and difficulties regulating emotions in general.
For more personality quizzes check this: How Many Kids Will I Have Quiz.